Flat Feet in Childhood Treated by Top Foot Surgeons in Baltimore
Our surgeons at The Institute for Foot and Ankle Reconstruction at Mercy specialize in diagnosing and treating children with flat feet. Our doctors provide bone grafting as one of the surgical treatment options for flat feet.
It used to be thought that nothing could be done to change the pattern of development of the child's flat foot. The difficulty is distinguishing those children whose feet are going to become problematic, painful and deformed from those children whose feet will remain flat but do not have symptoms associated with them.
There are a number of conditions in childhood and adolescence that can cause a flat foot. The most important issue in diagnosis of the condition is whether the foot, although flat, will remain flexible or whether it will become stiff or rigid. If the foot is rigid, the inward and outward movement (inversion and eversion) is lost.
During the first few years of life a flat foot is perfectly normal. It is only around the fourth or fifth year that the arch really begins to develop. Flat feet at this age rarely require any treatment. Only when the foot is very flat and shoes are wearing out rapidly is some sort of treatment required. For these children we use an orthotic arch support.
The arch support does not change the shape of the foot nor will it change the development of the foot in any way. It simply maintains the foot in a slightly better position in the shoe, making shoe wear a little easier. If the feet are still very flat by the time a child is eight years old, they can become symptomatic.
Children will complain of flat fee symptoms such as:
- Aching and fatigue in the arch of the feet and the legs
- Inability to "keep up" with other children in recreational and athletic activities
A foot and ankle specialist can diagnose flat feet in children by taking a medical history and conducting a physical exam.
Some children require treatment for the flexible flat foot if symptoms cannot be controlled with shoe changes and orthotic arch supports. There are two types of surgical treatments that have been quite successful:
- Insert a small cylindrical plug into the heel bone joint (the subtalar joint)
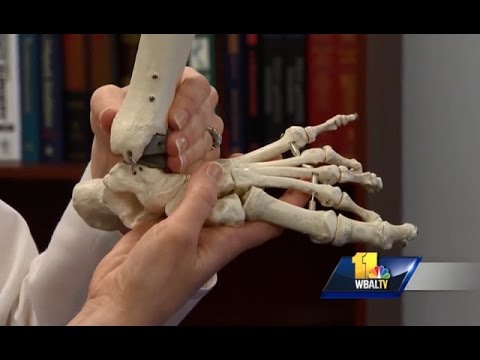
- Change the shape of the foot with bone cuts (an osteotomy) and combine this with the use of a bone graft
The insertion of the cylindrical plug (Maxwell-Brancheau Arthroerisis "MBA") is a device that has proven very successful in the correction of the child’s flat foot. The surgical procedure to insert the arthroerisis implant takes approximately 20 minutes and involves the insertion of a small cylindrical plug through a one centimeter incision on the outside of the heel and ankle.
The child is able to walk on the foot after a few days using either a short leg walking cast or removable walking boot, determined by comfort and sometimes any additional surgical procedures which may be performed simultaneously. The subtalar MBA implant is typically left in place forever and does not need to be removed.
As the foot gets more deformed, the subtalar implant may not be sufficient to correct the flat foot deformity. For these children a bone cut or osteotomy is made on the heel bone (the calcaneus) to elongate it and improve the arch of the foot. As the heel bone is lengthened, the gap in the bone is filled with bone graft. The child’s bone is not used and bone is taken from the bone bank.
There is negligible risk to using bone from the bone bank. It is far less painful than taking the child’s own bone and generally means shorter operating and anesthesia time with less blood loss. Our doctors provide the option of using these types of bone grafts in both adults and children.